Vue - vuex!
Vuex - 뷰 이벤트 상태관리자
vue 컴포넌트가 많아질수록 유지보수가 복잡해 진다.
간단한 어플리케이션의 경우 EventBus 나 옵션으로 로 데이터관리를 해도 상관 없지만
복잡해 질수록 vue 컴포넌트의 상태를 결정할 데이터를 한곳에 모아 집중관리할 필요가 있다.
이를 위해 Global 상태정보객체(전역 데이터 저장객체) 를 사용할 수 있다.
Vuex 같은 상태관리 라이브러리를 사용해 전역객채로 컴포넌트의 상태를 관리할 수 있다.
모든
vue 컴포넌트의 데이터를Vuex에서 관리할 필요는 없다.
구조
중앙 관리할 데이터(State)들이 저장될 저장소(Store) 객체 정의
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
increment(context) {
context.commit('increment')
}
}
})
vuex store 에서 주로 사용하는 필드는 아래와 같다.
statecommitdispatchgettersrootGettersrootState
Vuex 는 아래 그림과 같이 state, mutations, actions 를 관리한다.
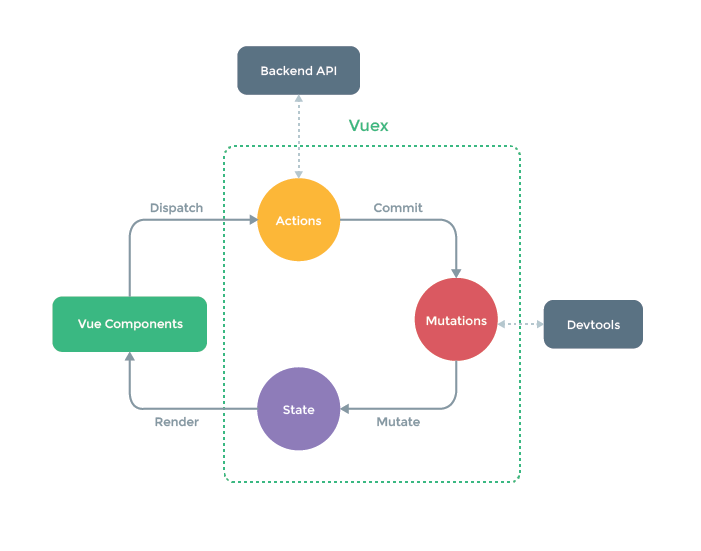
이벤트 발생에서 데이터 흐름을 보면 모두 한방향으로만 흐른다.
vue 컴포넌트가Action일으킴Action에서 외부 API 호출,Mutation(변이) 일으킴Mutation은Action의 결과를 받아State변경State는vue 컴포넌트에 바인딩되고 다시 랜더링
state,mutataions외에도actions,getters,module속성이 있는데 하나씩 알아보자.
this.$store 형식으로 각 컴포넌트에서 store 접근 지원을 위해 뷰 인스턴스 생성시 아래처럼 설정
state
상태(데이터) 를 저장하는 속성이다.
state 에 접근하려면 아래처럼 사용.
<div id="app">
<div>count: {{ count }}</div>
</div>
<script>
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { count: 0 }
})
var vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
computed: {
count() {
return store.state.count
}
}
})
</script>
mutation
mutations(변이) 속성에는 state 를 변경시키는 메서드를 정의한다.
store 내부에서 state 관련 코드를 확인하기 위해 state 값은 mutations 메서드로만 변경하는 것을 권장한다.
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { count: 0 }
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
}
})
store.commit() 명령으로 mutations 에 정의된 메서드 호출가능
기본적으로 state 를 파라미터로 전달받으며 다음과 같이 추가 파라미터(payload) 전달 가능
store.commit('increment', { amount:10 })
store.commit({ type: 'increment', amount:10 }) // 파라미터 합치기 가능
...
mutations: {
increment(state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount
}
}
commit은 변경된state를 동기화 시키는 역할을 한다.
Vuex에선 상태관리를 위해 모든 변이에 대해 상태의 “이전” 및 “이후” 스냅 샷을 캡처 해야하기 때문에 콜백형식의 비동기 처리방식은 변이에 적용 불가능하다.
actions
actions 는 state 로 특정작업을 수행하고 mutation 함수를 호출하는 경우 사용
axios 같은 비동기 호출문 결과를 status 에 넣어야 할 때
mutations 메서드를 직접호출하기 보단 actions 를 통해 비동기적으로 호출되는 것을 권장.
Pormise로 감싸기 때문에 시간이 오래걸리는 비동기적 처리방식에서actions속성 사용 권장
시간이 오래걸리는axios와 같이 자주 사용된다.
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
// 외부에서 Promise 로 감쌓음
increment(store) {
console.log(`count: ${store.state.count}`)
store.commit('increment')
}
}
})
store.dispatch() 명령으로 mutations 에 정의된 메서드 호출가능
기본적으로 vuex store 자체를 매개변수로 전달받으며 아래처럼 추가적으로 매개변수 전달 가능
store.dispatch('increment', { amount:10 })
store.dispatch({ type:'increment', amount:10 }) // 파라미터 합치기 가능
...
actions: {
increment(store, value) {
console.log(`value: ${value.amount}`)
store.commit('increment')
}
}
...
vuex store 자체를 매개변수로 받기 때문에 내부에서 다른 actions, mutations 메서드에 접근, 호출 가능하다.
actions 내부에서 특정필드만 사용한다면 디스트럭처링 문법 사용을 권장
actions: {
increment({ commit }) { // ES6 디스트럭처링
commit('increment')
}
}
getter
단순히 state 안의 데이터를 가져오는 것이 아닌 변조를 해야할 경우 getter 를 사용한다.
vue 컴포넌트의computed옵션과 비슷, 미리 연산해서 출력이 빠르다.
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: '...', done: false }
]
},
getters: {
doneTodos(state) {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
},
doneTodosCount(state, getters, rootState, rootGetters) {
return getters.doneTodos.length
}
}
})
console.log(store.getters.doneTodos)
// vuex store 의 getter 속성을 통해 접근가능
getters 에는 state, getters, rootState, rootGetters 를 가변적으로 인자로 받을 수 있다.
rootState,rootGetters는 아래 모듈에서 설명
plugins
store.dispatch 명령어로 state 를 업데이트한 후 서버에 해당 사실을 알리고 싶을 때
hook 과 같은 개념으로 plugins 옵션을 사용할 수 있다.
const myPlugin = store => {
store.subscribe((mutation, state) => {
console.log(mutation);
console.log(state.happy); // 30
})
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
happy: 40
},
mutations: {
happy_update(state) {
state.happy = 30
}
},
plugins: [myPlugin]
})
위와같이 store.subscribe 함수를 통해 plugins 구성 가능
store.commit 명령 실행하면 콘솔로그 가 출력됨을 알 수 있다.
모듈
관리할 vue 인스턴스, vue 컴포넌트 간 데이터 동기화를 위해 vuex store 를 사용했는데
관리해야할 vuex store 조차도 많아져 모듈화가 필요하게되었다.
모듈 방식을 통해 vuex store 들을 한곳으로 모아
아래처럼 vuex store 를 계층형으로 관리할 수 있다.
const moduleA = {
state: { count: 0 },
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
},
getters: {
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
}
}
}
const moduleB = {
state: { count2: 10 },
mutations: {
increment2(state) {
state.count2++
}
},
getters: {
doubleCount2(state, b, c, d) {
return state.count2 * 2
}
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {...},
mutations: {...},
actions: {...},
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
});
vuex store 가 모듈로 구성되면 모든 모듈의 state, getters 를 모아 rootState, rootGetters 로 구성한다.
때문에 각 모듈의 state, mutations, actions, getters 필드는 서로 다른이름을 가지고 있어야 한다(그렇지 않을경우 오류발생)
모듈 방식 사용시 모듈의 접두사정의 및 문자열을 상수화 적극사용권장
모듈 방식이 아닐경우state=rootState,getters=rootGetters
중복된 이름의 필드가 없음으로 기존 store.commit, store.dispatch, store.getters 호출방식은 동일하다
이미 생성된 vuex store 에 모듈을 추가하거나 제거할경우 아래 메서드를 사용
store.registerModule('a', moduleA);
store.unregisterModule('a');
추가 제안
모듈 구조
메서드 상수화
호출하는 mutations, actions 메서드는 별도의 상수형태의 문자열을 보관하는 것을 권장
const SOME_MUTATION = 'SOME_MUTATION';
var store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
lucky: 0
},
mutations: {
[SOME_MUTATION](state) {
console.log(state.lucky);
}
}
});
상수 문자열이 아예 별도 저장되도록 파일분리를 권장한다.
헬퍼메서드
각 컴포넌트들은 공유데이터 store.state 를 바로 사용하거나, 때에 따라선 store.getters 를 사용해 필터링해 가져온다.
공유데이터 store.state 를 변경하기 위해 store.mutations 속성에 각종 메서드들을 정의하고
commit 함수를 사용해 호출한다.
정의된 mutations 내부 메서드들은 actions 에서 호출된다.
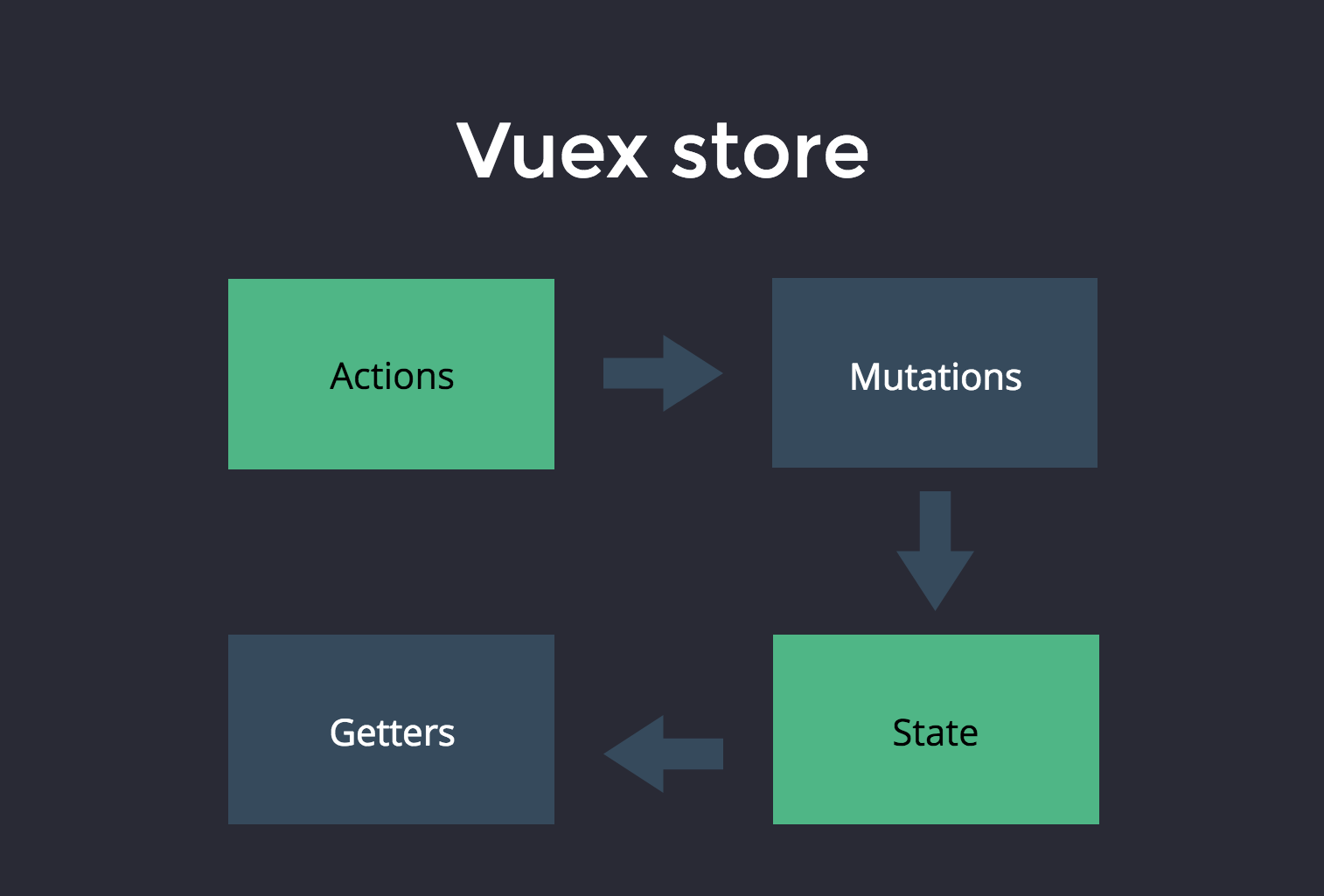
최종적으로 위와 같은 형식을 갖춘다.
vuex store 의 state, mutations, actions, getter 에 접근하기 위해 store 참조변수를 직접 사용했는데
vue 템플릿 내부에서 this.$store 와 같이 긴 문자를 가진 접근형식사용을 권장하지 않는다.
축약형 사용을 권장하며 아래처럼 매칭되는 헬퍼메서드를 사용해 별도의 메서드를 정의해 사용하는 것을 권장한다.
store.state - mapState
store.commit - mapMutations
store.dispatch - mapActions
store.getter - mapGetter
또한 헬퍼메서드를 사용하면 좀더 간단하게 state, mutations, actions, getter 를 바인딩해서 사용할 수 있다.
mapState
지금까지 store.state 를 data, computed 객체 속성과 매칭시키기 위해 function...return 을 사용해왔다.
computed: {
todolist: function() {
return this.$store.state.todolist;
}
}
mapState 메서드를 사용하면 단축 가능하다.
mapState를 사용하기 전 mapState 의 매개변수와 반환값을 알아보자.
매개변수로 리터럴객체 혹은 문자열배열이 들어갈 수 있다.
mapState([todoItem]);
/*
반환형식은 아래와 같다.
{ deleteTodo: function of store's state method... }
*/
mapState({myItems: "todoItem"});
/*
반환형식은 아래와 같다.
{ myItems: function of store's state method... }
*/
mapMutamapStatetions 는 state 를 가져오는 함수의 참조변수를 리터럴객체형식으로 반환하는 함수이다.
이후 설명할 mapMutations, mapGetters, mapActions 반환 형식 모두 동일하다.
todoItem 메서드를 사용하면 state 속성에 정의된 todoItem 가 호출된다.
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed: mapState(['todoItem'])
};
보동 computed 함수에는 다른 함수들도 많이 들어가기 때문에 스프레드 문법을 자주사용하는 편이다.
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['todoItem'])
}
};
mapMutations
store.mutations 속성에 정의된 메서드를 호출하기 위해 아래처럼 commit 를 사용해왔다.
methods: {
deleteTodo: function(id) {
this.$store.commit(Constant.DELETE_TODO, { id: id });
}
}
어차피 commit 의 첫번째 매개변수는 mutations 속성의 이름, 두번째 매개변수는 전달할 객체(payload)가 항상 고정적으로 들어간다.
이런 지루한 과정을 mapMutations 함수로 생략하자.
import { mapMutations } from "vuex";
export default {
methods: {
...mapMutations({removeTodo: "deleteTodo"})
}
};
mapState, mapMutations 모두 일반적인 호출방식과 사용법만 조금 다를뿐 기능은 동일하다.
mapMutations 를 사용하면 호출함수의 매개변수를 반드시 객체로 감싸야하는점이다.
removeTodo({...}) 처럼 매개변수에 리터럴객체 형식으로 보내야한다.
mapGetters
export const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todoItems: storage.fetch(),
},
getters: {
storedTodoItems(state) {
return state.todoItems;
}
}
})
getters 속성에 storedTodoItems 이라는 state.todoItems 값에 따라 데이터만 반환하는 메서드를 정의
일반적으로 getters 에 정의한 storedTodoItems 메서드로 반환된 데이터를 뷰 컴포넌트에서 등록하려면 아래 처럼 설정해왔다.
export default {
computed: {
todoItems() {
return this.$store.getters.storedTodoItems;
}
}
}
mapGetters 를 사용하면 아래처럼 단축 가능하다.
export default {
computed: {
...mapGetters({todoItems: "storedTodoItems"})
}
}
this.todoItems 형식으로 템플릿에서 접근 가능하다.
mapActions
mapMutations 과 마찬가지로 mapActions를 통해 actions 와 바인딩시켜 코드 생략이 가능하다.
함수명은 아래처럼 별도의 상수화 시켜놓는것을 권장한다.
methods: {
...mapActions([Constant.DONE_TOGGLE])
}
패턴
Flux
한방향으로만 data flow 하는 구조