Rest API
클라이언트가 특정 서비스로부터 HTTP 프로토콜을 통해 json 형식의 데이터를 가져오는 너무나도 당연한 형식의 코드를 Flutter 로 작성해보자.
http
https://flutter.dev/docs/cookbook#networking
Dart와 Flutter가 제공하는 http package 를 사용해 네트워크에서 데이터를 읽어와 보자.
아래 Url 에서 패키지 설치
https://pub.dev/packages/http
아래 형식으로 사용할 수 있다.
Future<http.Response> fetchPost() {
return http.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1');
}
URL이 반환하는 JSON 데이터
{ "userId": 1, "id": 1, "title": "sunt aut facere repellat provident occaecati excepturi optio reprehenderit", "body": "quia et suscipit\nsuscipit recusandae consequuntur expedita et cum\nreprehenderit molestiae ut ut quas totam\nnostrum rerum est autem sunt rem eveniet architecto" }
http.get() 메서드
Future<Response> get (dynamic url, {Map<String, String> headers})
url을 입력하면 Future<Response> 데이터 타입을 반환한다.
Future<T> class가 등장하는데 데이터를 위한 작은 선물상자로 생각하면 된다.
안에는 특정 value혹은 error가 있을 수 있다.
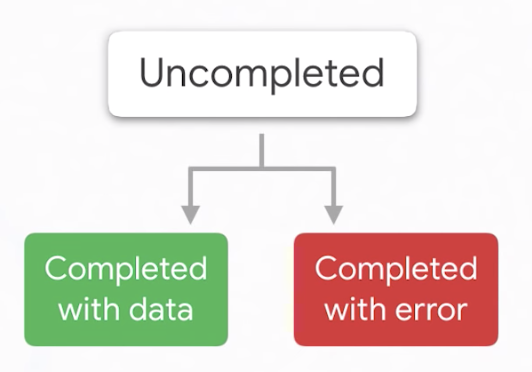
Future는 위 3가지 상태를 가지며 코드가 아직 실행되지 않은 Uncompleted상태, 코드가 실행된 Complete상태가 있다.
어쨋건 http.get으로 받은 http.Response객체를 우리가 원하는 데이터 형식으로 변환하면 된다.
http.get()외에도put,post,delete메서드를 지원한다.
Future<http.Response> updateAlbum(String title) {
return http.put(
'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/albums/1',
headers: <String, String>{
'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=UTF-8',
},
body: jsonEncode(<String, String>{
'title': title,
}),
);
}
json to Dart
Dart에선 JSON 데이터로 바로 사용하지 않고 별도의 객체를 정의하고 http.Response를 Post로 형변환 하자.
https://javiercbk.github.io/json_to_dart/
위 사이트를 통해 json 데이터와 매칭되는 클래스를 자동생성할 수 있다.
class Post {
int userId;
int id;
String title;
String body;
Post({this.userId, this.id, this.title, this.body});
Post.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
userId = json['userId'];
id = json['id'];
title = json['title'];
body = json['body'];
}
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() {
final Map<String, dynamic> data = new Map<String, dynamic>();
data['userId'] = this.userId;
data['id'] = this.id;
data['title'] = this.title;
data['body'] = this.body;
return data;
}
}
Future<Post> fetchPost() async {
final response = await http.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1');
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
return Post.fromJson(json.decode(response.body));
} else {
throw Exception('Failed to load post');
}
}
json.decode 를 사용하려면 아래 패키지를 import 해야한다.
import 'dart:convert';
mockito
간단히 Rest API를 테스트 하기위해 mockito 패키지를 사용할 수 있다.
https://pub.dev/packages/mockito
mockito 의 경우 dev_dependencies에서 추가한다.
dev_dependencies:
flutter_test:
sdk: flutter
mockito: ^4.1.1
test 디렉토리에 간단한 테스트 메서드 작성
http 패키지를 사용해 response를 가져오는 테스트 진행
// widget_test_http.dart
void main() {
test("http 통신 테스트", () async {
var response = await http.get("https://api.airvisual.com/v2/nearest_city?key=");
expect(response.statusCode, 200);
AirResult result = AirResult.fromJson(json.decode(response.body));
expect(result.status, "success");
});
}
Http status 가 200이 출력되는지 확인
전달받은 json 데이터 response.body를 AirResult dart객체로 변환하고 status 값이 success 문자열인지 확인
FutureBuilder
이제 전달받은 데이터를 페이지 위젯에 출력하기만 하면 된다.
이쯤에서 전체코드를 한번 봐보자.
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
Future<Post> fetchPost() async {
final response =
await http.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1');
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
return Post.fromJson(json.decode(response.body));
} else {
throw Exception('Failed to load post');
}
}
class Post {
final int userId;
final int id;
final String title;
final String body;
Post({this.userId, this.id, this.title, this.body});
factory Post.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return Post(
userId: json['userId'],
id: json['id'],
title: json['title'],
body: json['body'],
);
}
}
void main() => runApp(MyApp(post: fetchPost()));
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
final Future<Post> post;
MyApp({Key key, this.post}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Fetch Data Example',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Fetch Data Example'),
),
body: Center(
child: FutureBuilder<Post>(
future: post,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
if (snapshot.hasData) {
return Text(snapshot.data.title);
} else if (snapshot.hasError) {
return Text("${snapshot.error}");
}
return CircularProgressIndicator();
},
),
),
),
);
}
}
여기서 FutureBuilder<Post>라는 위젯을 통해 페이지를 생성하는데
async가 정의된 fetchPost()메서드는 동기화작업이 필요해도 페이지 위젯을 생성하고 화면에 띄우는 작업은 굳이 동기화 될 때 까지 기다릴 필요가 없다.
맨 처음 생성될 때에는 Future<Post>가 uncompleted상태임으로 return CircularProgressIndicator();가 수행되며 로딩 이미지를 출력한다.
snapshot.data를 통해 future속성에 설정된 post인스턴스에 접근이 가능하고 Future<Post>가 complete상태가 되면 다시한번 호출되며 post의 title을 출력한다.
snapshot은 AsyncSnapshot<T>로 데이터, 에러, 연결 상태 등을 확인할 수 있다.
https://api.flutter.dev/flutter/widgets/AsyncSnapshot-class.html
compute - Parse JSON in the background
사용자 인터페이스를 방해하지 않고 많은 양의 데이터를 백그라운드에서 처리할때 compute 메서드를 사용한다.
Future<http.Response> fetchPhotos(http.Client client) async {
return client.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/photos');
}
http.get 메서드는 사실
http.Client생성후client의get메서드를 호출하는 것이다.
위 url 요청시 5000장에 해당하는 이미지 JSON 데이터를 반환한다.
[
{
"albumId": 1,
"id": 1,
"title": "accusamus beatae ad facilis cum similique qui sunt",
"url": "https://via.placeholder.com/600/92c952",
"thumbnailUrl": "https://via.placeholder.com/150/92c952"
},
...
...
{
"albumId": 100,
"id": 5000,
"title": "error quasi sunt cupiditate voluptate ea odit beatae",
"url": "https://via.placeholder.com/600/6dd9cb",
"thumbnailUrl": "https://via.placeholder.com/150/6dd9cb"
}
]
이 JSON데이터를 사용하기 편하도록 Photo라는 우리가 정의한 객체로 형변환하는 작업을 compute 메서드를 사용해 처리해보자.
JSON Array -> List<Photo>
먼저 Photo클래스 정의,
class Photo {
final int id;
final String title;
final String thumbnailUrl;
Photo({this.id, this.title, this.thumbnailUrl});
factory Photo.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return Photo(
id: json['id'] as int,
title: json['title'] as String,
thumbnailUrl: json['thumbnailUrl'] as String,
);
}
}
위의 JSON Arraey를 List<Photo>로 형변환
List<Photo> parsePhotos(String responseBody) {
final parsed = json.decode(responseBody).cast<Map<String, dynamic>>();
return parsed.map<Photo>((json) => Photo.fromJson(json)).toList();
}
이 형변환 과정 parsePhotos 메서드를 compute 를 통해 별도의 스레드가 백그라운드에서 콜백형식으로 일을 맡아 수행한다.
Future<List<Photo>> fetchPhotos(http.Client client) async {
final response = await client.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/photos');
return compute(parsePhotos, response.body);
}
Work with WebSockets
웹 소켓 서버와 연결하려면 web_socket_channel package가 필요하다.
https://pub.dev/packages?q=web_socket_channel
pubspec.yaml에 dependencies를 추가.
import 'package:web_socket_channel/io.dart';
import 'package:web_socket_channel/web_socket_channel.dart';
...
...
final channel = IOWebSocketChannel.connect('ws://echo.websocket.org');
서버와 연결된 WebSocketChannel 객체가 생성된다.
생성된 WebSocketChannel객체로 message를 송, 수신하며
StreamBuilder 위젯을 통해 message를 수신하여 처리할 수 있다.
https://api.flutter.dev/flutter/widgets/StreamBuilder-class.html
StreamBuilder(
stream: widget.channel.stream,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
return Text(snapshot.hasData ? '${snapshot.data}' : '');
},
);
stream객체는 IOWebSocketChannel.connect() 메서드로 생성한 WebSocketChannel에서 가져올 수 있으며 builder속성에 메세지를 받으면 호출하는 콜백함수 역할을 할 메서드를 정의한다.
snapshot을 통해 받은 데이터, 연결상태, 에러발생 여부를 체크할 수 있다.
데이터를 서버에 전송하거나 연결을 종료할 때에는 WebSocketChannel 안의 WebSocketSink 객체를 사용한다. \
channel.sink.add('Hello!');
channel.sink.close();
전체코드
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
import 'package:web_socket_channel/io.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:web_socket_channel/web_socket_channel.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final title = 'WebSocket Demo';
return MaterialApp(
title: title,
home: MyHomePage(
title: title,
channel: IOWebSocketChannel.connect('ws://echo.websocket.org'),
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
final String title;
final WebSocketChannel channel;
MyHomePage({Key key, @required this.title, @required this.channel})
: super(key: key);
@override
_MyHomePageState createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
TextEditingController _controller = TextEditingController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
Form(
child: TextFormField(
controller: _controller,
decoration: InputDecoration(labelText: 'Send a message'),
),
),
StreamBuilder( //stream에 변화가 발생할때 마다 호출되는 메서드 정의
stream: widget.channel.stream,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
return Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 24.0),
child: Text(snapshot.hasData ? '${snapshot.data}' : ''),
);
},
)
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _sendMessage,
tooltip: 'Send message',
child: Icon(Icons.send),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
void _sendMessage() {
if (_controller.text.isNotEmpty) {
widget.channel.sink.add(_controller.text);
}
}
@override
void dispose() {
widget.channel.sink.close();
super.dispose();
}
}