Spring Boot - MapStruct, Validation!
MapStruct
최근 jhipster 를 사용하면서 자동으로 생성되는 스프링 부트의 구조 + 처음보는 라이브러리들을 학습중이다.
유명한 Mapper 라이브러리로 ModelMapper와 MapStruct 가 있으며
한국과 일본을 제외하곤 전 세계적으로 MapStruct 의 사용량이 많다.
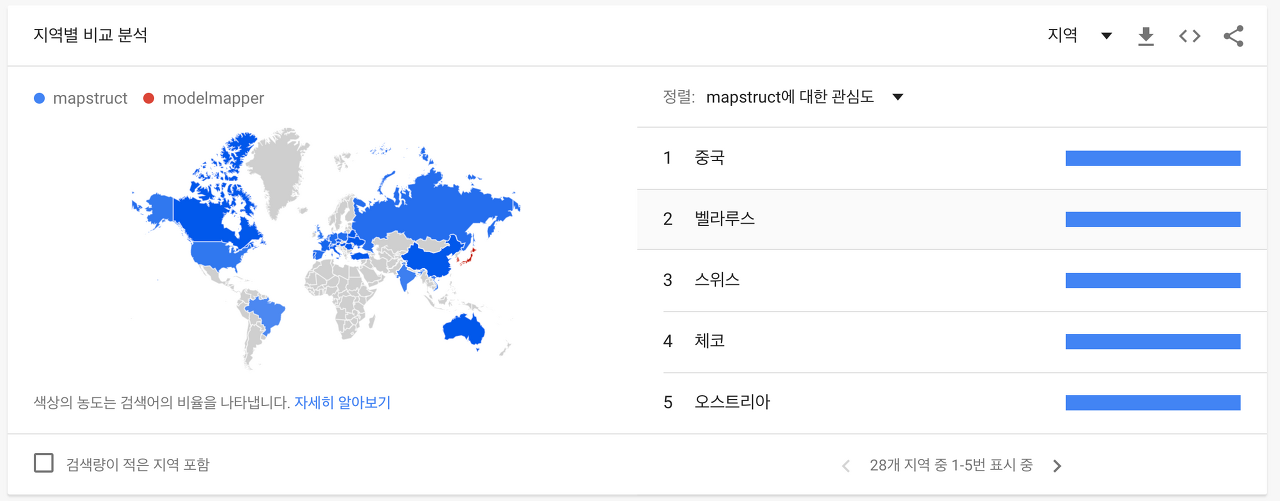
성능 또한 MapStruct 가 더 우세하다고 한다.
출처
https://yonguri.tistory.com/125
https://better-dev.netlify.app/java/2020/10/26/compare_objectmapper/
Usage
MapStruct 역시 Lombok 과 같이 annotation 을 기반으로 annotation processor 가 구현체를 auto generate 한다.
dependencies {
...
implementation 'org.mapstruct:mapstruct:1.4.2.Final'
annotationProcessor 'org.mapstruct:mapstruct-processor:1.4.2.Final'
}
아래와 같은 Car 객체를 매퍼를 사용해 CarDto 로 변경해야 할 경우
public class Car {
private String make;
private int numberOfSeats;
private CarType type;
//constructor, getters, setters etc.
}
public class CarDto {
private String make;
private int seatCount;
private String type;
//constructor, getters, setters etc.
}
MapStruct 라이브러리가 annotation processor 를 사용해 구현체를 만들수 있도록 @Mapper 어노테이션과 함께 interface 작성을 통해 정의해햐 한다.
@Mapper
public interface CarMapper {
CarMapper INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper( CarMapper.class );
@Mapping(source = "numberOfSeats", target = "seatCount")
CarDto carToCarDto(Car car);
}
매핑될 필드의 이름이 서로 다르더라도 @Mapping 어노테이션으로 처리 가능하다.
@Test
public void shouldMapCarToDto() {
//given
Car car = new Car( "Morris", 5, CarType.SEDAN );
//when
CarDto carDto = CarMapper.INSTANCE.carToCarDto( car );
//then
assertThat( carDto ).isNotNull();
assertThat( carDto.getMake() ).isEqualTo( "Morris" );
assertThat( carDto.getSeatCount() ).isEqualTo( 5 );
assertThat( carDto.getType() ).isEqualTo( "SEDAN" );
}
EntityMapper
jhipster 를 사용하면 좀더 효율적으로 스프링부트에서 MapStruct 작성을 할 수 있도록 여러 인터페이스를 자동 작성해주는데
Car 를 예제로 들면 아래처럼 수정해서 사용할 수 있다.
// D: dto, E: entity
public interface EntityMapper<D, E> {
E toEntity(D dto);
D toDto(E entity);
List<E> toEntity(List<D> dtoList);
List<D> toDto(List<E> entityList);
@Named("partialUpdate")
@BeanMapping(nullValuePropertyMappingStrategy = NullValuePropertyMappingStrategy.IGNORE)
void partialUpdate(@MappingTarget E entity, D dto);
// null value 는 dto -> entity 업데이트시에 적용하지 않는다.
// @MappingTarget 으로 데이터 매핑 방향 설정
}
Entity와 Dto 마다 인터페이스를 재정의해야 한다는 단점이 있지만
필드명이 똑같을경우 재정의 필요 없이 EntityMapper 상속만으로 대부분의 함수는 자동 생성되어 개발자의 실수를 줄여준다.
Car 클래스와 같이 Mapping 할 필드명이 많이 다를경우 아래처럼 모든 함수를 재정의해주어야 한다.
@Mapper(componentModel = "spring", uses = {})
public interface CarMapper extends EntityMapper<CarDto, Car> {
@Mapping(source = "seatCount", target = "numberOfSeats")
@Mapping(source = "carId", target = "id", ignore = true)
Car toEntity(CarDto carDto);
@Mapping(source = "id", target = "carId")
@Mapping(source = "numberOfSeats", target = "seatCount")
CarDto toDto(Car car);
@Named("partialUpdate")
@BeanMapping(nullValuePropertyMappingStrategy = NullValuePropertyMappingStrategy.IGNORE)
@Mapping(source = "carId", target = "id", ignore = true)
@Mapping(source = "seatCount", target = "numberOfSeats")
void partialUpdate(@MappingTarget Car entity, CarDto dto);
default Car fromId(Long id) {
if (id == null) {
return null;
}
Car car = new Car();
car.setId(id);
return car;
}
}
매핑 필드명이 달라 재정의해야할 경우
EntityMapper 에 정의했던 어노테이션은 덮어씌어짐으로 모두 다시 작성해주어야 한다.
componentModel = "spring" 속성을 통해 Spring 프로젝트에서 bean 으로 등록해준다.
빌드가 완료되면 build 디렉토리에 아래와 같은 Mapper 구현체가 생성된다.
@Generated(
value = "org.mapstruct.ap.MappingProcessor",
date = "2021-06-16T16:00:13+0900",
comments = "version: 1.4.2.Final, compiler: IncrementalProcessingEnvironment from gradle-language-java-7.0.2.jar, environment: Java 11.0.10 (GraalVM Community)"
)
@Component
public class CarMapperImpl implements CarMapper {
@Override
public List<Car> toEntity(List<CarDto> dtoList) {
if ( dtoList == null ) {
return null;
}
List<Car> list = new ArrayList<Car>( dtoList.size() );
for ( CarDto carDto : dtoList ) {
list.add( toEntity( carDto ) );
}
return list;
}
@Override
public List<CarDto> toDto(List<Car> entityList) {
if ( entityList == null ) {
return null;
}
List<CarDto> list = new ArrayList<CarDto>( entityList.size() );
for ( Car car : entityList ) {
list.add( toDto( car ) );
}
return list;
}
@Override
public Car toEntity(CarDto carDto) {
if ( carDto == null ) {
return null;
}
Car car = new Car();
car.setNumberOfSeats( carDto.getSeatCount() );
car.setMake( carDto.getMake() );
if ( carDto.getType() != null ) {
car.setType( Enum.valueOf( CarType.class, carDto.getType() ) );
}
return car;
}
@Override
public CarDto toDto(Car car) {
if ( car == null ) {
return null;
}
CarDto carDto = new CarDto();
carDto.setCarId( car.getId() );
carDto.setSeatCount( car.getNumberOfSeats() );
carDto.setMake( car.getMake() );
if ( car.getType() != null ) {
carDto.setType( car.getType().name() );
}
return carDto;
}
@Override
public void partialUpdate(Car entity, CarDto dto) {
if ( dto == null ) {
return;
}
if ( dto.getSeatCount() != null ) {
entity.setNumberOfSeats( dto.getSeatCount() );
}
if ( dto.getMake() != null ) {
entity.setMake( dto.getMake() );
}
if ( dto.getType() != null ) {
entity.setType( Enum.valueOf( CarType.class, dto.getType() ) );
}
}
}
컨트롤러나 서비스 클래스에서 어래처럼 사용할 수 있다.
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("/car")
public class CarController {
private final CarRepository carRepository;
private final CarMapper carMapper;
@PostMapping
CarDto setCar(@RequestBody CarDto carDto) {
Car car = carMapper.toEntity(carDto);
carRepository.save(car);
return carMapper.toDto(car);
}
@PatchMapping("{id}")
CarDto patchCar(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody CarDto carDto) {
Car car = carRepository.findById(id).get();
carMapper.partialUpdate(car, carDto);
car = carRepository.save(car);
return carMapper.toDto(car);
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public CarDto getCar(@PathVariable Long id) {
Car car = carRepository.findById(id).get();
return carMapper.toDto(car);
}
}
Mapstruct With Setter
DDD 개발 구조에선 Entity 클래스에 Setter 함수 정의를 피한다.
하지만 MapStruct 의 partialUpdate 메서드는 Entity 에 Setter 메서드가 정의되어 있어야 한다.
결론은 Setter 메서드없이 partialUpdate 하는 방법은 없다.
만약 DDD 구조에서 MapStruct 를 사용하고 싶다면 partialUpdate 메서드는 정의하지 말아야 한다.
어차피
DDD특성상update함수를 애그리거트 클래스에서 정의함으로 큰 부담을 아닐것이다.
String Validator
참고
https://meetup.nhncloud.com/posts/223
http://www.thejavageek.com/2014/05/24/jpa-constraints/
https://beanvalidation.org/
@Valid - 칼럼에 대한 각종 제약조건 설정
| 어노테이션 | 설명 | 사용예 |
|---|---|---|
@AssertFalse |
값이 무조건 false 여야함 |
@AssertFalse boolean isUnsupported; |
@AssertTrue |
값이 무조건 true여야함 | @AssertTrue boolean isActive; |
@DecimalMax |
10진수 최대값이 n값 이하 실수여야함 | @DecimalMax(“30.00”) BigDecimal discount; |
@DecimalMin |
10진수 최소값이 n값 이하 실수여야함 | @DecimalMin(“5.00”) BigDecimal discount; |
@Digits |
정수와 실수 자리수 지정 | @Digits(integer=6, fraction=2) BigDecimal price; |
@Future |
해당날짜가 현재보다 미래여야함 | @Future Date eventDate; |
@Past |
해당 날짜가 현재보다 과거여야함 | @Past Date birthday; |
@Max |
n값 이하여야함 | @Max(10) int quantity; |
@Min |
n값 이상이어야함 | @Min(5) int quantity; |
@NotNull |
값이 null일수 없음 | @NotNull String username; |
@Null |
값이 null이어아햠 | @Null String unusedString; |
@Pattern |
정규식을 만족해야함 | @Pattern(regexp=”(d{3})d{3}-d{4}”) String phoneNumber; |
@Size |
최소크기, 최대크기를 지정 | @Size(min=2, max=240) String briefMessage; |
어노테이션 내부 groups 필드를 사용하면 특정 조건에 맞춰서 검증을 진행시킬 수 있다.
public interface Ad {
}
public class Message {
// groups 가 javax.validation.groups.Default 로 지정되어 있을때만 검증 진행
@Length(max = 128)
@NotEmpty
private String title;
@Length(max = 1024)
@NotEmpty
private String body;
// groups 가 Ad 로 지정되어 있을때만 검증 진행
@Length(max = 32, groups = Ad.class)
@NotEmpty(groups = Ad.class)
private String contact;
// groups 가 Default, Ad 로 지정되어 있을때만 검증 진행
@Length(max = 64, groups = {Default.class, Ad.class})
@NotEmpty(groups = Ad.class)
private String removeGuide;
}
@Validated(Ad.class) // 메서드 호출 시 Ad 그룹이 지정된 제약만 검사한다.
public void sendAdMessage(@Valid Message message) {
// Do Something
}
// @Validated(javax.validation.groups.Default ) 가 정의되어있는것과 동일하다.
public void sendNormalMessage(@Valid Message message) {
// Do Something
}
Validation Message
Custom Validation
검증할 조건을 커스텀하게 작성 가능하다.
입력값이 해당 CustomEnum 에 부합하는지를 검증하고 싶을때,
public enum CustomEnum {
INFO, WARN, ERROR, DEBUG;
@JsonValue
public String getValue() {
return this.name();
}
@JsonCreator
public static CustomEnum fromString(String value) {
for (CustomEnum customEnum : values()) {
if (customEnum.name().equals(value))
return customEnum;
}
return null;
}
}
@Getter
@Setter
public class MyCustomValidDto {
@AssertFalse
private Boolean isFalse;
@NotBlank(message = "should be not null")
private String msg1;
@ValidCustomEnum // 검증할 문자열, enum 과 부합하는지
private String enumValue;
}
아래와 같이 Constraint 를 적용한 어노테이션을 사용해서 검증조건을 커스텀하게 정의할 수 있다.
@Documented // java doc 에 포함
@Constraint(validatedBy = CustomEnumValidator.class)
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ValidCustomEnum {
String message() default "is invalid enum type";
// 검증 그룹 지정
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
// 주로 Payload 를 구현하는 클래스를 정의해서 사용한다, 동적 처리를 위한 추가정보로 사용함
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
// String 입력값을 기준으로 enum 과 비교한다.
class CustomEnumValidator implements ConstraintValidator<ValidCustomEnum, String> {
private List<String> enumNames;
@Override
public void initialize(ValidCustomEnum constraintAnnotation) {
enumNames = Arrays.stream(CustomEnum.values())
.map(customEnum -> customEnum.name())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
if (value == null) {
return false; // null 값은 에러
}
for (String enumName : enumNames) {
if (enumName.equals(value)) {
return true; // 입력된 값이 Enum에 존재하는 경우 유효
}
}
return false; // 입력된 값이 Enum에 존재하지 않는 경우 유효하지 않음
}
}
클래스단위 Custom Validation
클래스의 특정필드가 특정값일 때만 검증하고 싶을때,
클래스 위에 Custom Validation 을 위한 어노테이션을 지정해서 설정할 수 있다.
아래와 같이 groups 로 검증조건을 지정하고, isAd=true 일 경우 검증하도록 설정할 수 있다.
// 단순 마커용 인터페이스
public interface Ad { }
@AdMessageConstraint // 클래스단위 커스텀 검증 어노테이션
public class Message {
@Length(max = 128)
@NotEmpty
private String title;
@Length(max = 1024)
@NotEmpty
private String body;
@Length(max = 32, groups = Ad.class)
@NotEmpty(groups = Ad.class)
private String contact;
@Length(max = 64, groups = Ad.class)
@NotEmpty(groups = Ad.class)
private String removeGuide;
private boolean isAd; // 광고 여부를 설정할 수 있는 속성
}
validator.validate 함수에서 Ad.class groups 조건을 추가해서 설정 가능하다.
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = {AdMessageConstraintValidator.class})
@Documented
public @interface AdMessageConstraint {
String message() default "invalid param in ad condition";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
class AdMessageConstraintValidator implements ConstraintValidator<AdMessageConstraint, Message> {
private Validator validator;
// 생성자 초기화 필수
public AdMessageConstraintValidator(Validator validator) {
this.validator = validator;
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(Message value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
if (value.isAd()) {
// 위반한 검증 목록
final Set<ConstraintViolation<Object>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(value, Ad.class);
if (constraintViolations != null && constraintViolations.size() != 0) {
// 기본 메시지 제거하고 새로운 MethodArgumentNotValidException 에 message 에 정의된 문자열를 넣는 과정
context.disableDefaultConstraintViolation();
constraintViolations.stream()
.forEach(constraintViolation -> context
.buildConstraintViolationWithTemplate(constraintViolation.getMessageTemplate()) // 에러메세지 삽입
.addPropertyNode(constraintViolation.getPropertyPath().toString())
.addConstraintViolation());
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Enum Validation
특정 필드가 Enum 타입과 일치해야 하는 값을 가져야할 경우에도 동일하게 ConstraintValidator 를 사용할 수 있다.
public enum TestType {
HELLO,
WORLD,
FOO,
BAR
}
@Getter
@Setter
public class EnumRequestDto {
@ValidEnum(target = TestType.class)
private String type;
}
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = {EnumValidator.class})
@Documented
public @interface ValidEnum {
String message() default "invalid param for enum";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
Class<? extends Enum> target();
}
class EnumValidator implements ConstraintValidator<ValidEnum, String> {
Enum[] enumValues;
@Override
public void initialize(ValidEnum constraintAnnotation) {
enumValues = constraintAnnotation.target().getEnumConstants();
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
if (value == null) return true;
return Arrays.stream(enumValues).filter(it ->
it.name().equals(value)
).findAny().isPresent();
}
}
RequestParam & SpEL
myapp:
default-page-size: 10
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Value("${myapp.default-page-size}")
private int defaultPageSize;
@GetMapping("/example")
public String getExample(
@RequestParam(name = "pageSize", defaultValue = "#{${myapp.default-page-size}}") int pageSize) {
return "Page size: " + pageSize;
}
}
@… 을 사용하면 bean 으로 등록되어 있는 configuration 에서 값을 가져와 사용할 수 도 있다.
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "myapp")
public class MyAppProperties {
private int defaultPageSize = 10;
public int getDefaultPageSize() {
return defaultPageSize;
}
public void setDefaultPageSize(int defaultPageSize) {
this.defaultPageSize = defaultPageSize;
}
}
@RestController
public class MyController {
private final MyAppProperties properties;
@Autowired
public MyController(MyAppProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@GetMapping("/example")
public String getExample(
@RequestParam(name = "pageSize", defaultValue = "#{@myAppProperties.defaultPageSize}") int pageSize) {
return "Page size: " + pageSize + ", App name: " + properties.getAppName();
}
}
Kotlin Validation
data class CreateCustomerRequest(
@field:NotEmpty(message = "username is required")
val username: String,
@field:NotEmpty(message = "password is required")
var password: String?,
@field:NotEmpty
var nickname: String,
@field:NotEmpty
var name: String,
var birth: String,
)
위와 같은 data class 를 @Valid @RequestBody 로 수신받을 때,
username 을 빼면 org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableException 에러가 발생하고
password 를 빼면 org.springframework.web.bind.support.WebExchangeBindException 에러가 발생한다.
username 의 경우 not null property 로 정의되어 있어 json 을 dto 로 변환하는 과정에서 에러가 발생하고
password 의 경우 nullable property 로 정의되어 있어 Validation 처리에서 예외가 발생한다.
WebFlux 에선
HttpMessageNotReadableException대신org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebInputException에러가 발생함.
아래와 같이 기본값을 추가하면 json 변환에서 not null 로 인한 오류는 뜨지 않고 validation 로직을 수행한다.
하지만 null 로 값을 설정할수 없기 때문에 반쪽자리 코드이긴 하다.
@field:NotEmpty(message = "username is required")
val username: String = "",
@field:NotEmpty(message = "password is required")
var password: String = "",
굳이 validation 로직을 수행할 필요없이 에러 응답을 수행하려면 HttpMessageNotReadableException 내부 cause 필드를 이용할 수 있다.
@ExceptionHandler(value = [HttpMessageNotReadableException::class])
fun handleException(e: HttpMessageNotReadableException): ResponseEntity<ErrorResponseDto> {
val description = when (val cause = e.cause) {
is MismatchedInputException -> "${cause.path.joinToString { it.fieldName }} 필드에 값이 없습니다."
else -> messageSource.getMessage("error.BAD_REQUEST", null, Locale.getDefault())
}
return ResponseEntity(
ErrorResponseDto(
code = ErrorCode.BAD_REQUEST.code,
error = ErrorCode.BAD_REQUEST.error,
description = description
), HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST
)
}
cause.path.joinToString 을 통해 depth 가 깊은 필드도 참조할 수 있다. compute.resourceLimit.cpu 와 같은 형태
WebFlux의ServerWebInputException에선 에러발생 유발, 필드이름을 가져오는 방법이 없음으로 기본값 사용을 통해validation처리해야 할듯.
데모 코드
https://github.com/Kouzie/spring-boot-demo/tree/main/mapper-demo