Spring Boot - 직렬화!
ObjectMapper
스프링에는 @RestController 등을 사용하여 HTTP Body 안의 문자열을 클래스로 변환 할때 ObjectMapper 를 사용한다.
Jackson 라이브러리가 기본으로 Spring boot starter web 에 포함되어 있기 때문.
해당 라이브러리에선 ObjectMapper Bean 뿐 아니라 각종 Json 관련 어노테이션 등도 제공한다.
스프링부트에서 ObjectMapper 의 커스텀 properties 설정을 제공한다.
spring.jackson.###
예를들어 json 네이밍 전략을 SNAKE 나 CAMEL 로 변경하고 싶다면 아래와같이 설정 가능
spring.jackson.property-naming-strategy=SNAKE_CASE
spring.jackson.property-naming-strategy=CAMEL_CASE
java config 를 사용해 별도로 ObjectMapper 빈으로 등록하면
기존 생성되는 ObjectMapper 를 대체할 수 도 있다.
public static class ZonedDateTimeDeserializer extends JsonDeserializer<ZonedDateTime> {
@Override
public ZonedDateTime deserialize(JsonParser jsonParser, DeserializationContext deserializationContext) throws IOException {
return ZonedDateTime.parse(jsonParser.getText(), formatter);
}
}
@Bean
public ObjectMapper objectMapper() {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// for zone date time
SimpleModule module = new JavaTimeModule()
.addSerializer(ZonedDateTime.class, new ZonedDateTimeSerializer(formatter))
.addDeserializer(ZonedDateTime.class, new ZonedDateTimeDeserializer());
objectMapper.registerModule(module);
objectMapper.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone(zoneId));
// for Date class
objectMapper.setDateFormat(dateFormat);
// WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS JSON에서 날짜를 문자열로 표시
objectMapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);
objectMapper.setPropertyNamingStrategy(PropertyNamingStrategies.LOWER_CAMEL_CASE); // 네이밍 전략
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL); // null 필드는 변환 X
// UnrecognizedPropertyException 처리, 알수없는 필드 처리 X
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
// InvalidDefinitionException, Object 클래스는 빈 객체로 변환(필드가 없는 객체도 변환하도록)
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false);
// {}, [] 같은 빈 json 객체를 null 로 변환처리
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.ACCEPT_EMPTY_ARRAY_AS_NULL_OBJECT, true)
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.ACCEPT_EMPTY_STRING_AS_NULL_OBJECT, true)
return objectMapper;
}
Visibility
[getter, setter, is-getter, creator, field] 에 대해 json 구성에서 visibility 여부를 결정할 수 있는데 기본설정은 아래와 같다.
protected final static Std DEFAULT = new Std(
Visibility.PUBLIC_ONLY, // getter
Visibility.PUBLIC_ONLY, // is-getter
Visibility.ANY, // setter
Visibility.ANY, // creator -- legacy, to support single-arg ctors
Visibility.PUBLIC_ONLY // field
);
[setter, creator] 는 접근제어자가 public 이 아니어도 상관없지만
[getter, is-getter, field] 는 public 이 아닐경우 보이지 않는다는 설정이기에 json 이 별도처리하지 않는다
최근에는 setter 와 같은 메서드를 별도정의하지 않기 때문에 field 값만 가지고 json 역질렬화를 수행하기 위해 아래와 같은 설정을 하기도 한다.
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.FIELD, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
Coercion
가끔 List, Object 형식의 데이터를 역직렬화 해야 하는데 "" empty string 으로 올 경우 아래와 같은 에러가 출력될 떄가 있다.
Cannot coerce empty String ("") to element of `java.util.ArrayList<java.lang.String>`
mapper.coercionConfigFor(MyPojo.class) // MyPojo 에 대해서 적용
.setCoercion(CoercionInputShape.EmptyString, CoercionAction.AsEmpty);
mapper.coercionConfigDefaults() // 기본 설정으로 적용
.setCoercion(CoercionInputShape.EmptyString, CoercionAction.AsEmpty);
CoercionAction.AsEmpty는{}
CoercionAction.AsNull는null
Json Annotation
Jackson 라이브러리에 수많은 json 관련 어노테이션이 있지만
자주 사용하는것 몇가지만 소개하고자 한다.
@JsonCreator, @JsonValue
@Getter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public enum SearchType {
USERNAME("username"),
TYPE("type"),
TITLE("title");
private final String key;
@JsonCreator
public static SearchType forValue(String key) {
for (SearchType value : values()) {
if (value.getKey().equals(key)) {
return value;
}
}
return null;
}
@JsonValue
public String toValue() {
return key;
}
}
enum 클래스의 경우 변환할때 enum 인스턴스가 가지고있는 name 을 value 로 사용하게 되는데
key 값을 가지고 enum 인스턴스를 serialize, deserialize 하고 싶다면 위와같이 사용
ObjectMapper 의 writeValueAsString 를 호출하게 되면 @JsonValue 에 설정된 문자열이 반환된다.
@JsonProperty
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class Board {
private String title;
private String username;
@JsonProperty("Type")
private String type;
}
일반적으로 Json 필드의 문자열은 네이밍 전략을 철저히 따라 생성해야 하지만
특정 필드 하나만 특별한 사유로 다른 네이밍 전략을 사용하고 싶을때
위와같이 @JsonProperty 어노테이션을 사용하면 좋다.
기본 value 필드 외에도 index 를 지정하거나 access 를 통해 접근제한, required 옵션을 통해 validation 구성도 가능하니 상세 구현페이지 참고
@JsonNaming
@Getter
@Setter
@JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategies.SnakeCaseStrategy.class)
public static class WeatherData {
private String weather;
private String weatherCd;
private String rainy;
private String maxTemperature;
private String minTemperature;
}
Jackson 에서 제공하는 ObjectMapper 의 기본 네이밍 전략은 lower camel case 이다.
만약 특정 클래스의 네이밍 전략만 snake case 로 변경하고 싶다면 @JsonNaming 어노테이션 사용하면 된다.
기본생성자 없이 역직렬화
ObjectMapper 에선 기본생성자를 통해 객체를 생성하고 setter 를 통해 필드값을 설정하는 방법으로 역직렬화를 수행한다.
기본생성자를 생성할 수 없는 경우에 역직렬화 하는 방법들을 알아본다.
// JSON 데이터
public static String json = "{\"username\":\"john_doe\", \"email\":\"john@example.com\"}";
public static class CustomUser {
public String username;
public String email;
public CustomUser(String username, String email) {
this.username = username;
this.email = email;
}
}
parameter-names 모듈 등록
public static class CustomUser {
public String username;
public String email;
public CustomUser(String username, String email) {
this.username = username;
this.email = email;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws JsonProcessingException {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// parameter-names 등록
objectMapper.registerModule(new ParameterNamesModule());
// 역직렬화
CustomUser user = objectMapper.readValue(json, CustomUser.class);
}
@JsonCreater @JsonProperty 사용
public static class CustomUser {
public String username;
public String email;
@JsonCreator
public CustomUser(@JsonProperty("username") String username,
@JsonProperty("email") String email) {
this.username = username;
this.email = email;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws JsonProcessingException {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 역직렬화
CustomUser user = objectMapper.readValue(json, CustomUser.class);
}
Mixin 클래스 사용
public static class CustomUser {
public String username;
public String email;
public CustomUser(String username, String email) {
this.username = username;
this.email = email;
}
}
public static class CustomUserMixin {
CustomUserMixin(@JsonProperty("username") String username,
@JsonProperty("email") String email) {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws JsonProcessingException {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 믹스인 등록
objectMapper.addMixIn(CustomUser.class, CustomUserMixin.class);
// 역직렬화
CustomUser user = objectMapper.readValue(json, CustomUser.class);
}
다형성 지원 - @JsonTypeInfo, @JsonSubTypes
아래와 같이 [id, notificationType, userId, message, timestamp] 까지는 동일하지만 그 뒤의 일부 필드만 다를 경우 사용 가능하다.
[
{
"id": "60d5dbf87f3e6e3b2f4b2b3a",
"notificationType": "message",
"userId": "1",
"message": "You have a new message from Alice",
"timestamp": "2023-08-01T10:00:00Z",
"senderId": 2
},
{
"id": "60d5dbf87f3e6e3b2f4b2b3b",
"notificationType": "friend_request",
"userId": "1",
"message": "Bob sent you a friend request",
"timestamp": "2023-08-01T10:05:00Z",
"requesterId": 3
},
{
"id": "60d5dbf87f3e6e3b2f4b2b3c",
"notificationType": "event_invite",
"userId": "1",
"message": "You are invited to Sarah birthday party",
"timestamp": "2023-08-01T10:10:00Z",
"eventId": 5,
"location": "123 Main St"
}
]
아래와 같이 Notification 클래스의 상속구조로 구성하고 jackson 의 @JsonTypeInfo, @JsonSubTypes 어노테이션을 사용해 비직렬화시 다형성을 지원할 수 있다.
가끔 json 문자열을 지원하는 라이브러리에서 @class, @type 같은 필드를 가지는 경우 해다 어노테이션을 사용한 경우이다.
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@JsonTypeInfo(
use = JsonTypeInfo.Id.NAME,
property = "notificationType",
include = JsonTypeInfo.As.EXISTING_PROPERTY,
visible = true // type 정보도 출력할건지 여부
)
@JsonSubTypes({
@JsonSubTypes.Type(value = Notification.MessageNotification.class, name = "message"),
@JsonSubTypes.Type(value = Notification.FriendRequestNotification.class, name = "friend_request"),
@JsonSubTypes.Type(value = Notification.EventInviteNotification.class, name = "event_invite")
})
@AllArgsConstructor
public abstract class Notification {
private String id;
private String notificationType;
private String userId;
private String message;
private Instant timestamp;
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public static class MessageNotification extends Notification {
private Long senderId;
public MessageNotification(String id, String notificationType, String userId, String message, Instant timestamp, Long senderId) {
super(id, notificationType, userId, message, timestamp);
this.senderId = senderId;
}
}
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public static class FriendRequestNotification extends Notification {
private Long requesterId;
public FriendRequestNotification(String id, String notificationType, String userId, String message, Instant timestamp, Long requesterId) {
super(id, notificationType, userId, message, timestamp);
this.requesterId = requesterId;
}
}
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public static class EventInviteNotification extends Notification {
private Long eventId;
private String location;
public EventInviteNotification(String id, String notificationType, String userId, String message, Instant timestamp, Long eventId, String location) {
super(id, notificationType, userId, message, timestamp);
this.eventId = eventId;
this.location = location;
}
}
}
- JsonTypeInfo
- use: 타입 정보를 어떤 형식으로 나타낼지를 지정
JsonTypeInfo.Id.NAME: 사전 정의된 별칭 사용.JsonTypeInfo.Id.CLASS: 클래스 전체 이름 사용.JsonTypeInfo.Id.MINIMAL_CLASS: 축약된 클래스 이름 사용.JsonTypeInfo.Id.CUSTOM: TypeIdResolver 사용.
- property: 타입 정보를 저장할 JSON 속성의 이름을 지정, 별도지정 안하면 아래 문자열을 사용함.
@class,JsonTypeInfo.Id.CLASS인 경우.@type,JsonTypeInfo.Id.NAME인 경우.
- include: 타입 정보를 JSON에 어떤 방식으로 포함할지 지정.
JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY: 클래스 정보를 JSON 객체의 특정 속성사용.JsonTypeInfo.As.EXISTING_PROPERTY: 클래스 정보를 내부에 이미 정의된 속성으로 사용.JsonTypeInfo.As.EXTERNAL_PROPERTY: 클래스 정보를 JSON 객체 외부의 별도 속성으로 저장.JsonTypeInfo.As.WRAPPER_OBJECT: 클래스 정보를 별도의 래핑(wrapping) 객체로 저장.JsonTypeInfo.As.WRAPPER_ARRAY: 클래스 정보를 배열의 첫 번째 요소로 저장.
- visible: 다형성 지원 필드로 비직렬화에 출력시킬지 여부.
- use: 타입 정보를 어떤 형식으로 나타낼지를 지정
// EXTERNAL_PROPERTY
{
"type": "com.example.MyClass",
"data": {
"name": "Example Name",
"value": 42
}
}
// WRAPPER_OBJECT
{
"com.example.MyClass": {
"name": "Example Name",
"value": 42
}
}
// WRAPPER_ARRAY
[
"com.example.MyClass",
{
"name": "Example Name",
"value": 42
}
]
아래와 같이 다형성 처리된 JSON 문자열을 전달해도 jackson 이 정확하게 비직렬화 한다.
@PostMapping
public void sendNotification(@RequestBody List<Notification> notifications) {
// 받은 notifications를 처리하는 로직 추가
notifications.forEach(notification -> {
// 예시로 각 알림의 'type'을 출력하는 로직
log.info("Received notification of type: " + notification.getNotificationType());
log.info(notification.toString());
});
}
/*
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/mapper \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '[
{
"id": "60d5dbf87f3e6e3b2f4b2b3a",
"notificationType": "message",
"userId": "1",
"message": "You have a new message from Alice",
"timestamp": "2023-08-01T10:00:00Z",
"senderId": 2
},
{
"id": "60d5dbf87f3e6e3b2f4b2b3b",
"notificationType": "friend_request",
"userId": "1",
"message": "Bob sent you a friend request",
"timestamp": "2023-08-01T10:05:00Z",
"requesterId": 3
},
{
"id": "60d5dbf87f3e6e3b2f4b2b3c",
"notificationType": "event_invite",
"userId": "1",
"message": "You are invited to Sarah birthday party",
"timestamp": "2023-08-01T10:10:00Z",
"eventId": 5,
"location": "123 Main St"
}
]'
*/
Date Time String
시간값을 표현하는 방식은 time format 을 통해 결정된다.
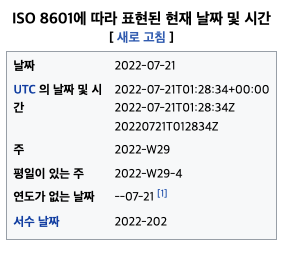
현재 날짜를 표기하는 문자열로 전 세계 공통으로 사용하는 format 은 ISO 8601 이다.
위키: ISO 8601 은 날짜 및 시간 관련 데이터 의 전 세계적인 교환 및 통신을 다루는 국제 표준 입니다.
큰 시간 기간(일반적으로 1년)이 왼쪽에 배치되고 연속적으로 작은 각 기간이 이전 기간의 오른쪽에 배치되도록 정렬
특정 의미가 할당된 특정 컴퓨터 문자(예: “-“, “:”, “+”, “T”, “W”, “Z”)의 조합으로 작성된 문자열을 뜻합니다.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_8601
이중 ISO 8601 의 가장 많이 사용하는 format 문자열은 LocalTimeFormat 을 표현하는 yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss 이다.
스프링에서 DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME 를 formatter 로 사용하면 된다.
public static final DateTimeFormatter ISO_DATE_TIME;
static {
ISO_DATE_TIME = new DateTimeFormatterBuilder()
.append(ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME) // yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS
.optionalStart()
.appendOffsetId() // 'Z', "+HH:MM:ss"
.optionalStart()
.appendLiteral('[')
.parseCaseSensitive()
.appendZoneRegionId() // zone id
.appendLiteral(']')
.toFormatter(ResolverStyle.STRICT, IsoChronology.INSTANCE);
}
각종 optional 조건들을 사용하여 ZoneDateTime, LocalDateTime 포멧 상관없이 웬만한 문자열을 날짜객체로 desieralize 한다.
하지만 serialize 의 경우 아래와 같이 출력된다.
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME;
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println(dtf.format(zonedDateTime));
// 2022-07-22T00:37:36.368955+09:00[Asia/Seoul]
따라서 serialize 용 Formatter 는 직접 만들어 ObjectMapper Serializer 에 설정하는 것을 권장
// 2022-08-10T10:36:50+09:00
private static DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormat =
DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssXXX").withZone(zone);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// for zone date time
SimpleModule module = new JavaTimeModule()
.addSerializer(ZonedDateTime.class, new ZonedDateTimeSerializer(dateTimeFormat))
.addDeserializer(ZonedDateTime.class, new ZonedDateTimeDeserializer());
objectMapper.registerModule(module);
objectMapper.setTimeZone(zone);
Time Format String
DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME 와 같이 미리 제공된 Formatter 말고
직접 타임포멧문자열 을 사용해서 Formatter 를 생성하고 싶다면 날짜를 표현하는 여러가지 문자 및 기호를 알아야 한다.
아래 url 참고
format 을 Optional 하게 설정하고 싶다면 [, ] 특수문자를 사용,
yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss[.SSS] - 나노초가 있을수도 없을수도 있다
ZonedDateTime zdt = ZonedDateTime.now();
String[] pattern = {
"G", // 서기 연대 (BC, AD)
"y", // 2017 년도
"M", // 6 월 (1~12 또는 1월~12월)
"q", // 2 분기(quarter)
"w", // 24 년의 몇 번째 주 (1~53)
"W", // 3 월의 몇 번째 주 (1~5)
"D", // 163 년의 몇 번째 일 (1~366)
"d", // 12 월의 몇 번째 일 (1~31)
"F", // 5 월의 몇 번째 요일 (1~5)
"e", // 2 요일
"a", // 오후 오전/오후 (AM/PM)
"H", // 15 시간 (0~23)
"h", // 3 시간 (1~12)
"k", // 15 시간 (1~24)
"K", // 3 시간 (0~11)
"m", // 53 분 (0~59)
"s", // 4 초 (0~59)
"S", // 5 1/1000초 (0~999)
"A", // 57184516 1/1000초 (그 날의 0시 0분 0초 부터의 시간)
"n", // 516000000 나노초 (0~999999999)
"N", // 57185416000000 나노초 (그 날의 0시 0분 0초 부터의 시간)
"z", // KST 시간대 ID(VV)
"O", // GMT+9 시간대(Time zone) 이름
"Z", // +0900 지역화된 zone-offset
"x", // +09 zone-offset
"XX", // +0900 zone-offset(Z는 +00:00를 의미)
"XXX", // +09:00
};
for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length; i++) {
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(pattern[i]);
System.out.println(zdt.format(dtf));
}
TemporalAccessor
TemporalAccessor 를 사용하면 아래와 같이 LocalDateTime 과 ZoneDateTime 포멧 문자열을 모두 다룰 수 있다.
LocalDateTime 문자열을 ZoneDateTime 포멧으로 변경시도하면 에러가 발생하는데
객체 변환 전에 Offset 정보가 있는지 미리 확인 후 문자열 포멧에 맞는 날짜객체로 변환한다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
String time1 = "2011-12-03T10:15:30";
ZonedDateTime zdt1 = convertAllString(time1);
String time2 = "2011-12-03T10:15:30Z";
ZonedDateTime zdt2 = convertAllString(time2);
System.out.println(zdt1.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME)); // 2011-12-03T10:15:30+09:00[Asia/Seoul]
System.out.println(zdt2.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME)); // 2011-12-03T10:15:30Z
}
public static ZonedDateTime convertAllString(String isoDateTime) {
TemporalAccessor accessor = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME.parse(isoDateTime);
if (accessor.isSupported(ChronoField.OFFSET_SECONDS)) {
return ZonedDateTime.from(accessor);
} else {
// return LocalDateTime.from(accessor).atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Seoul"));
return LocalDateTime.from(accessor).atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
}
}
@DateTimeFormatter
요청파라미터 에서 문자열을 바로 날짜 객체로 변환하고 싶을때 @DateTimeFormat 어노테이션을 사용
@GetMapping("/board")
List<BaordRequestDto> getBoard(@PathVariable Long deviceId,
@DateTimeFormat(iso = DateTimeFormat.ISO.DATE_TIME) @RequestParam LocalDateTime beginDate,
@DateTimeFormat(iso = DateTimeFormat.ISO.DATE_TIME) @RequestParam LocalDateTime endingDate);
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class TestRequestDto {
private String title;
private String type;
@DateTimeFormat(iso = DateTimeFormat.ISO.DATE_TIME)
private ZonedDateTime beginDate;
@DateTimeFormat(iso = DateTimeFormat.ISO.DATE_TIME)
private ZonedDateTime endingDate;
}
설명은 아래와 같이 적혀있다.
@DateTimeFormat: The most common ISO Date Time Format yyyy-MM-dd’T’HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX — for example, “2000-10-31T01:30:00.000-05:00”.
아래와 같은 controller 클래스를 생성하고 curl 명령을 전송해보자.
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class GetController {
@GetMapping
public Object testGet(@Valid TestRequestDto requestDto) {
log.info(requestDto.toString());
return requestDto;
}
}
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X GET "http://localhost:8080/test?title=testTitle&type=testType&beginDate=2019-09-01T09:00:00+9:00&endingDate=2019-09-02T09:00:00+9:00"
{
"timestamp": "2021-08-18T13:38:01.738+00:00",
"status": 400,
"error": "Bad Request",
"path": "/test"
}
서버 로그에는 대충 아래와 같은 로그가 출력되는데
default message [Failed to convert property value of type 'java.lang.String' to required type 'java.time.ZonedDateTime' for property 'beginDate'
...
Parse attempt failed for value [2019-09-01T09:00:00 9:00]]<EOL>Field error in object 'testRequestDto' on field 'endingDate'
대충 봐도 request parameter parsing 에 실패한 것을 알 수 있다.
그리고 서버가 해독한 URL 내의 날짜 데이터 부분이 이상한 것을 알 수 있다.
이번엔 +09:00 부분은 Z 로 교체한 후 request 해보자.
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X GET "http://localhost:8080/test?title=testTitle&type=testType&beginDate=2019-09-01T09:00:00Z&endingDate=2019-09-02T09:00:00Z"
{
"title": "testTitle",
"beginDate": "2019-09-01T09:00:00Z",
"endingDate": "2019-09-02T09:00:00Z",
"type": "testType"
}
성공하는 것으로 보아 @DateTimeFormat 어노테이션은 정상작동 하고 있는 것을 알수 있고
URL 의 디코딩 문제로 유추할 수 있다.
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X GET "http://localhost:8080/test?title=testTitle&type=testType&beginDate=2019-09-01T09%3A00%3A00%2B09%3A00&endingDate=2019-09-02T09%3A00%3A00%2B09%3A00"
{
"title": "testTitle",
"beginDate": "2019-09-01T09:00:00Z",
"endingDate": "2019-09-02T09:00:00Z",
"type": "testType"
}
URL 에서 + 기호는 공백을 표기하기도 하기에 위처럼 인코딩 과정을 거친 후 보내면 정상동작한다.
Zulu time 을 사용하였을 때에도 URL 을 인코딩 하는 것을 권장한다. 브라우저나 서버 프레임워크별로 차이가 있을 수 있음.
Converter
String time = "2011-12-03T10:15:30";
// Text '2011-12-03T10:15:30' could not be parsed: Unable to obtain ZonedDateTime from TemporalAccessor
ZonedDateTime zdt = ZonedDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println(zdt.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME));
보다싶이 ZoneDateTime 은 문자열에 ZoneId 가 없으면 파싱과정에서 에러가 발생한다.
이는 @DateTimeFormat 어노테이션을 사용해 파싱할 때도 똑같이 발생한다.
위와 같이 LocalDateTime 형식의 문자열이 들어올 경우 시스템, 혹은 사용자 별도 지정한 ZoneId 를 사용해
ZoneDateTime 을 생성하도록 Converter 를 생성해보자.
org.springframework.core.convert 패키기의 Converter 클래스를 사용해
직접 String -> ZoneDateTime 할 수 있는 클래스를 만들기로 했다.
@Slf4j
public class ZonedDateTimeConverter implements Converter<String, ZonedDateTime> {
@Override
public ZonedDateTime convert(String source) {
log.info("Parsing string {}", source);
return convertAllString(source);
}
public static ZonedDateTime convertAllString(String isoDateTime) {
DateTimeFormatter parser = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME;
TemporalAccessor accessor = parser.parse(isoDateTime);
if (accessor.isSupported(ChronoField.OFFSET_SECONDS)) {
return ZonedDateTime.from(accessor);
} else {
// return LocalDateTime.from(accessor).atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Seoul"));
return LocalDateTime.from(accessor).atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
}
}
}
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
registry.addConverter(new ZonedDateTimeConverter());
}
}
보다싶이 입력받은 시간 문자열에 OFFSET 이 없다면 LocalDateTime 으로 변환 후 System 의 ZondId 를 삽입하여 반환하도록 설정했다.
@GetMapping("/simple/local")
public Object testSimpleLocalGet(@RequestParam ZonedDateTime zdt) {
zdt = zdt.withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
log.info(zdt.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_OFFSET_DATE_TIME));
return zdt.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_OFFSET_DATE_TIME);
}
$ curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X GET "http://localhost:8080/test/simple/local?zdt=2019-09-02T09:00:00"
2019-09-02T00:00:00Z%
$ curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X GET "http://localhost:8080/test/simple/local?zdt=2019-09-02T09:00:00Z"
2019-09-02T09:00:00Z%