JSP/Servlet - MVC패턴!
모델2 구조의 MVC패턴
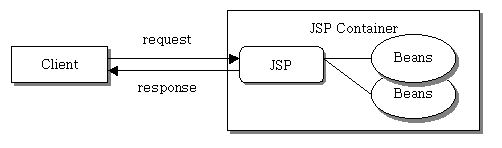
웹 개발은 모델1 구조와 모델2 구조로 나뉜다.
모델1구조는 하나의 jsp페이지에서 모든 작업을 처리하는 구조이다.
만약 클라이언트가 emp테이블의 모든 정보를 출력해주는 페이지를 요청한다면
요청받은 jsp파일은 데이터를 가져와서 while문 돌며 출력까지,
모든 작업을 하나의 jsp파일에서 처리한다.
반면 모델 2는 처리하는 작업을 분담해 두었다.
요청은 무조건 서블릿 객체가 받는다.
이 요청을 받는 서블릿 객체를 Controller라 한다.
Controller는 받은 요청에 따라 각 로직을 처리해야 하는데 처리하는 객체가 별도로 존재한다.
각 로직을 처리하는 객체를 Model이라 한다.
Model객체가 로직을 처리하면 나온 결과값이 있을텐데 이 결과값을 DTO객체 등으로 담아서 Controller에게 반환한다.
Controller는 이 결과값을 클라이언트에게 보여줘야 하기 때문에 jsp파일에 포워딩 시키고
jsp파일은 이쁘게 출력버퍼에 담아 클라이언트에게 출력한다.
이쁘체 출력해주는 jsp파일을 View라 할 수 있다.
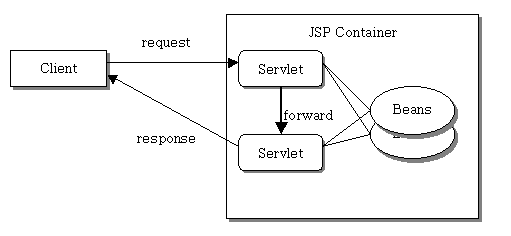
1~5 단계 과정을 잘 기억해 두자…
즉 모델 2구조는 응답받고, 로직처리하고, 출력하는 역할을 따로 나눠 두었는데 이런 구조를 따르기 위한 패턴을 MVC패턴이라 한다.
| MVC | 설명 | 처리담당 |
|---|---|---|
Model |
비지니스 영역의 로직을 처리한다. | 로직처리 클래스, 자바빈(DTO) |
View |
비지니스 영역에 대한 사용자가 보게될 결과 화면을 담당한다. | JSP |
Controller |
사용자 입력 처리와 흐름제어를 담당한다. | 서블릿 |
MVC의 컨트롤러 - 서블릿이 하는 역할

출처: https://dlsdn73.tistory.com/591
서블릿이 하는 역할을 총 5가지.
요청을 받아 분류하고
분류한 대로 모델에 일을 맡기고
결과를 받아 뷰에 출력을 맡긴다.
간단한 모델 2구조 컨트롤러 구현
<a href="/jspPro/days10/simple">simple</a><br>
<a href="/jspPro/days10/simple?type=date">simple_date</a><br>
<a href="/jspPro/days10/simple?type=greeting">simple_greeting</a><br>
<a href="/jspPro/days10/simple?type=admin">simple_admin</a><br>
a태그를 누르면 type파라미터 값에 따라 각각 다른 작업을 처리하는 서블릿 객체(Controller)를 만들어보자.
먼저 web.xml에 매핑해주자.
<!-- web.xml -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SimpleController</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>days10.mvc.simple.SimpleController</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SimpleController</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/days10/simple</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
days10.mvc.simple패키지 안에 SimpleController 서블릿 객체가 모든 요청을 처리해줄 Controller이다!
/* SimpleController.java */
public class SimpleController extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1단계 요청받음
processRequest(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
private void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException
{
//2단계 요청파악
String type = request.getParameter("type");
//3단계 요청에 따른 기능 수행
Object resultObject = null;
if (type == null || type.equals("greeting")) {
resultObject = "안녕하세요,";
}
else if (type.equals("date")) {
resultObject = new Date();
}
else {
resultObject = "Invalid Type";
}
//4단계 처리결과 저장
request.setAttribute("result", resultObject);
//5단계 포워딩
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("/days10/simpleView.jsp");
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
}
}
아주간단한 Controller,
로직 처리를 Model객체 생략하고 if문을 사용하였다.
if (type == null || type.equals("greeting")) {
resultObject = "안녕하세요,";
}
else if (type.equals("date")) {
resultObject = new Date();
}
else {
resultObject = "Invalid Type";
}
그리고 출력데이터 resultObject를 request에 저장하고 View역학을 하는 /days10/simpleView.jsp로 포워딩 시킨다.
/* simpleView.jsp */
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<%= request.getParameter("type") %> - ${ result }
</body>
</html>
각 type의 출력값
결과: 안녕하세요,
date - Thu May 09 16:57:24 KST 2019
greeting - 안녕하세요,
admin - Invalid Type
커맨드 패턴 기반 컨트롤러
MVC패턴에선 클라이언트의 모든 요청의 Controller역할을 하는 서블릿 클래스가 받는다.
서블릿 클래스는 이 요청을 분류하고 처리를 위해 로직담당인 Model객체에게 넘겨 주어야 하는데
이 요청을 분류하는 방법이 2가지 있다.
- 커맨드 패턴 기반
- URL명령 기반
먼저 커맨드 패턴 기반은 요청에 대한 분류를 위해 URL뒤에 파라미터로 명령값을 넘긴다.
위에서 보았던 SimpleController의 처리방식과 비슷하다.
<a href="controllerUsingFile?cmd=hello">hello</a><br>
a태그의 href속석을 보면 cmd 파라미터 값으로 hello를 넘긴다.
일단 controllerUsingFile을 처리하는 서블릿 객체(Controller)를 생성하고 web.xml에서 매핑해주자.
<!-- web.xml -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ControllerUsingFile</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>days10.mvc.controller.ControllerUsingFile</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>configFile</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/commandHandler.properties</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ControllerUsingFile</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/days10/controllerUsingFile</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
Controller역할을 하는 서블릿은 톰캣 실행과 동시에 메모리에 올라가고(load-on-startup) 파라미터로
SimpleController과 다른점이 /WEB-INF/commandHandler.properties 파일을 사용하는 것이다.
commandHandler.properties의 내용은 아래와 같다.
hello=days10.mvc.hello.HelloHandler
#somecmd=anySomeHandler
hello란 cmd파라미터 값이 들어온다면 days10.mvc.hello패키지에 있는 HelloHandler에게 처리를 맡기기 위한 properties파일이다.
즉 commandHandler.properties는 각각의 요청을 Model역할을 하는 Handler클래스와 이어주는 설정파일이다.
이제 새로운 요청(cmd)이 추가되거나 요청에 대한 Model이 변경된다면 commandHandler.properties내용만 변경해주면 된다.
서블릿 객체가 메모리에 올라가는 시점에 호출되는 init()메서드 안에
commandHandler.properties내용을 읽어 <요청종류-Model객체>형식의 Entry를 가지는 HashMap 콜렉션을 보관하도록 하자.
/* ControllerUsingFile */
public class ControllerUsingFile extends HttpServlet{
private Map<String, CommandHandler> commandHandlerMap = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
String configFile = getInitParameter("configFile");
Properties prop = new Properties();
String configFilePrath = getServletContext().getRealPath(configFile);
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(configFilePrath))
{
prop.load(fis);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
Iterator<Object> keyiter = prop.keySet().iterator();
while (keyiter.hasNext()) {
String command = (String) keyiter.next();
String handlerClassName = prop.getProperty(command);
try {
Class<?> handlerClass = Class.forName(handlerClassName);
CommandHandler handlerInstance = (CommandHandler) handlerClass.newInstance();
commandHandlerMap.put(command, handlerInstance);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
}
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
process(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
process(request, response);
}
private void process(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String command = request.getParameter("cmd");
// 요청 분류
CommandHandler handler = commandHandlerMap.get(command);
if (handler == null) {
handler = new NullHandler(); //404에러를 응답하는 핸들러 클래스
}
String viewPage = null;
try {
//요청에 따른 Model객체의 처리메서드 호출
viewPage = handler.process(request, response);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
if(viewPage != null) {
//요청 메서드가 반환한 데이터와 주소를 사용해 view로 포워딩
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(viewPage);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
}
}
}
Properties: https://kouzie.github.io/java/java-HashSet,-TreeSet,-HashMap,-TreeMap,-Properties!/#properties
Map안의 요소 type이 CommandHandler이다.
CommandHandler는 모든 들이 구현하는 인터페이스이다.
모든 이벤트 처리용 Model 객체들은 CommandHandler인터페이스를 구현하고 있다.(다형성을 활용한 예)
/* CommandHandler */
public interface CommandHandler {
public String process(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
cmd 파라미터가 commandHandler.properties에 등록되지 않은 요청이거나 입력되지 않았다면 commandHandlerMap은 null을 반환하고 NullHandler가 요청을 처리한다.
/* NullHandler */
public class NullHandler implements CommandHandler {
@Override
public String process(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
return null;
}
}
404에러를 의도적으로 일으킨다.
우리가 commandHandler.properties에 등록한 요청과 함께 hello값의 cmd파라미터가 들어온다면
설정파일에 따라 등록된 days10.mvc.hello.HelloHandler가 요청을 처리한다.
public class HelloHandler implements CommandHandler {
@Override
public String process(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
request.setAttribute("hello", "안녕하세요");
return "/WEB-INF/view/hello.jsp";
}
}
Model역할을 하는 HelloHandler는 요청 처리결과를 request에 담고 View역할을 하는 jsp의 주소 /WEB-INF/view/hello.jsp를 Controller에게 반환한다.
WEB-INF폴더 안에 파일을 넣어두면 외부에서 바로 jsp파일을 접근하지 못한다.
만약WebContent폴더 안에 저장한다면/localhost/jspPro/hello.jsp을 url로 입력하면 바로 접속 가능하다.
/* hello.jsp */
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<%= request.getAttribute("hello") %>
</body>
</html>
- 클라이언트가 서버(
Controller)에게cmd파라미터에hello를 담아 요청 Controller는 요청에 대한Model을 이미Map으로 관리하고 있고Model의process()메서드 호출Model의process()에선 처리값을request객체에 담고 출력할View주소를Controller에게 반환Controller는 반환받은View주소를 사용해 포워딩,requset에 저장해 놓은 최종 결과를 출력
안녕하세요가 출력된다!
커맨드 기반 방식의 핵심은
각각의 요청을 Model역할을 하는 Handler클래스와 이어주는 작업이라 할 수 있다.
요청 URI명령 기반 컨트롤러
커맨드 기반에선 처리할 행동을 cmd 파라미터에 저장해서 요청했지만
URI명령 기반에선 url만으로 처리할 행동을 표현한다.
아래와 같은 형식이 URI에 포함되어 있다면 컨트롤러가 전달받은 URI형식에 따라 각각의 Model역할을 하는 핸들러 클래스를 호출해야 한다.
<a href="/jspPro/board/list.do">list.do</a><br> <!-- 게시글 목록 출력 -->
<a href="/jspPro/board/regist.do">regist.do</a><br> <!-- 게시글 작성 -->
URI기반은 커맨드 기반에서 파라미터가 URL뒤의 붙는 문자열로 바뀌었을 뿐 크게 달라진점은 없다.
일단 새로 컨트롤러 역할을 해줄 서블릿 클래스를 정의하자
public class ControllerUsingURI extends HttpServlet{
...
...
//ControllerUsingFile과 doGet, doPost, init() 메서드는 완벽히 동일하다.
private void process(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//String command = request.getParameter("cmd");
String command = request.getRequestURI();
if (command.indexOf(request.getContextPath()) == 0) {
command = command.substring(request.getContextPath().length());
}
System.out.println(command);
CommandHandler handler = commandHandlerMap.get(command);
if (handler == null) {
handler = new NullHandler(); //404에러를 응답하는 핸들러 클래스
}
String viewPage = null;
try {
viewPage = handler.process(request, response);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
if(viewPage != null) {
String prefix = "/WEB-INF/view";
viewPage = prefix + viewPage;
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(viewPage);
System.out.println(viewPage);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
}
}
}
요청받은 URI를 자라서 request.getContextPath()는 생략하고 URI에 포함된 뒤의 값들만 command라는 문자열로 보관한다.
나머지는 커맨드 기반 패턴과 똑같다!
HashMap에서 command와 일치하는 핸들러 클래스(Model)을 찾아서 처리결과를 받고 View역할을 하는 jsp주소를 받아서 포워딩 시킨다.
String prefix = "/WEB-INF/view";은 혹여 view역할을 하는 jsp파일의 실제 위치가 변경되면 수월한 유지보수를 위해 별도로 정의해 놓은것.
따라서 commandHandler.properties에는 URI 뒷부분에 해당하는 설정을 추가해 주어야 한다.
/board/list.do=days10.mvc.board.ListHandler
/board/regist.do=days10.mvc.board.RegistHandler
각 URI 요청에 해당하는 핸들러 클래스를 등록!
그리고 당연히 web.xml에 Controller역할을 하는 ControllerUsingURI클래스를 매핑해야 한다.
*.do로 입력되는 모든 요청을 ControllerUsingURI가 처리하도록 설정…
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ControllerUsingURI</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>days10.mvc.controller.ControllerUsingURI</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>configFile</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/commandHandler.properties</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ControllerUsingURI</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>