java 예외처리!
Java의 예외처리
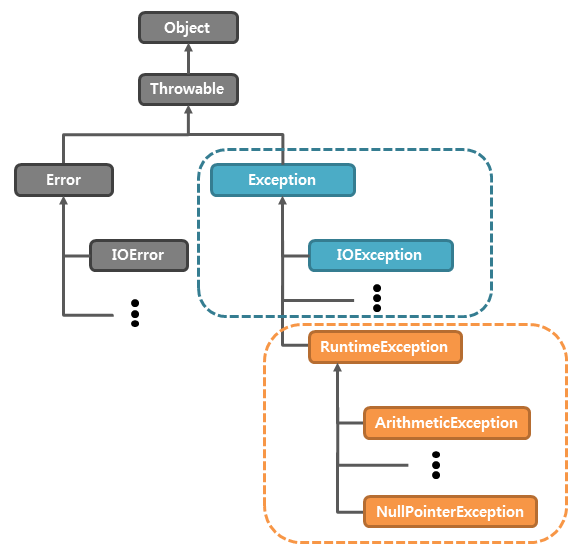
- java.lang.Exception
프로그램 코드에 의해서 수습될 수 있는 다소 미약한 오류 - java.lang.Error
프로그램 실행중 어떤 원인에 의해 오작동, 비정상 종료되는경우, 주로 JVM(Java Virtual Machine)에서 발생하는 심각한 문제.
OutOfMemoryError 가 대표적
java 에는 예외를 처리하기 위한 클래스(예외클래스)들이 있고 이 클래스들은 당연히 Object, Throwable 를 상속한다.
오류가 발생하면 자바실행기가 발생한 예외정보를 위의 예외처리객체로 개발자에게 전달해주고 받은 객체를 기반으로 예외를 처리한다.
이러한 예외처리 클래스 계층구조를 보면 Runtime Error를 리하기위한 RuntimeException클래스
그걸 상속하는 ArithemticException(0으로나누기), NullPointException 등이 있고
RuntimeException클래스는 Exception클래스를 상속한다.
아래 코드는 간단한 정수 입력 함수이다.
만약 정수대신 문자열을 넣으면 어떻게 할까
public class Ex04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = getNum();
System.out.println(num);
}
private static int getNum() {
@SuppressWarnings({"resource" })
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("num input: ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
return num;
}
}
정수대신 문자 입력시 출력
Exception in thread "main" java.util.InputMismatchException
at java.util.Scanner.throwFor(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.next(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Unknown Source)
at days18.Ex04.getNum(Ex04.java:16)
at days18.Ex04.main(Ex04.java:7)
java.util.InputMismatchException 라는 예외처리 클래스가 반환됐다.
try catch
1. try catch 사용하기
private static int getNum() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = 0;
System.out.print("num input: ");
try {
num = sc.nextInt();
}
catch(InputMismatchException e) {
num = -1;
}
return num;
}
2. throw 사용하기
private static int getNum() throws InputMismatchException {
//그냥 예외발생하면 호출한놈에게 떠넘기기
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = 0;
System.out.print("num input: ");
num = sc.nextInt();
num = -1;
return num;
}
물론 throw로 떠넘기면 결국 어디선가는 해결해줘야한다.
밑의 예처럼 main으로 throw하면 main에서 처리해줘야된다….
물론 또 던져도 된다… (그럼 처리하지 못하고 빨강색 글씨가 출력되겠지만….)
public class Ex04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 0;
try {
num = getNum(); //떠넘겨진 예외처리
}
catch (InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("오류발생!");
num=-1;
}
System.out.println(num);
}
...
}
try에서 예외가 발생하면 catch문을 수행하고 종료하는 것이 아닌 밑의 코드를 계속 실행한다. num출력하고 프로그램 종료
3. catch 예외 컨트롤
try {
result = a/b;
m[3] = 100;
System.out.println(m[3]);
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("> ArithmeticException 예외 처리.");
}
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("> ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 예외 처리.");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("> 어떤 예외든 여기 걸립니다....");
}
try {
result = a/b;
m[3] = 100;
System.out.println(m[3]);
}
catch (ArithmeticException | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { //합치기
System.out.println("> ArithmeticException & ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException예외 처리.");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("> 어떤 예외든 여기 걸립니다....");
}
여기서 쓰는 |는 OR연산자가 아니라 일종의 기호이다.
catch문에서만 위처럼 사용할 수 있다.
모든 예외클래스의 최상위 부모클래스인 Exception을 사용하면 어떤 오류건 잡아낼수 있다.
보통 다중캐치문에서 끝내 잡지 못한 예외처리용으로 맨 마지막 catch문으로 사용한다.
finally
try {
result = a/b;
m[3] = 100;
System.out.println(m[3]);
}
catch (ArithmeticException | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("> ArithmeticException & ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException예외 처리.");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("> ArithmeticException 예외 처리.");
}
finally {
System.out.println("finally 실행");
}
finally연산자는 예외가 발생하던 안하던 무조건 실행하는 구문이다.
보통 DB연결객체, 파일연결객체 등 연결해제구문이 finally에 들어간다.
연결객체를 만들었으면 무조건 해제해야한다.
안그러면 다른 프로세스가 해당 파일이나 DB에 접근할때 피해받는다.
그래서 도중에 예외가 발생해 프로그램 종료 위기가 있다 하더라도 연결객체 해제는 꼭 해주기 위해 finally를 사용한다.
그럼 예로 파일 연결용 객체를 만들어서 예외처리 해보자.
FileReader fr = null;
try
{
String fileName = "C:\\Class\\java\\학생명단.txt";
fr = new FileReader(fileName);
while((n = fr.read())!=-1) //읽은 문자가 없다면 -1 반환
{
System.out.print((char)n);
}
return; //이 리턴이 실행되어도 finally가 실행되고 프로그램이 종료된다.
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) //FileReader 인스턴스만드려면 해줘야하는 예외처리
{
e.printStackTrace();
e.getMessage(); //에러메시지를 가져옴(반환형 String)
}
catch (IOException e) //fread하려면 해줘야하는 예외처리
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
try
{
fr.close();
}
catch (IOException e) //fclose하려면 해줘야하는 예외처리
{
e.printStackTrace();
e.getMessage(); //에러메시지를 가져옴(반환형 String)
}
}
java에서 파일 읽기, 쓰기 작업은 FileReader로 파일 연결객체를 만들고 연결한다.
연결객체는 항상 인스턴스화 하려면 예외처리를 해줘야 한다.
도중에 예외가 발생해 연결객체를 닫지 못하는 상황을 없애기 위해서.
이번엔 throws를 통해 예외처리를 해보자.
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NullPointerException {
FileReader fr = null;
String fileName = "C:\\Class\\javaclass\\javaPro\\src\\days19\\학생명단.txt";
fr = new FileReader(fileName);
int n = fr.read(); //더이상 읽을게 없다면 -1을 반환한다.
System.out.print((char)n);
while((n = fr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)n);
}
fr.close();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("> END <");
}
try catch가 없어지면서 간결해졌지만 main에서조차 예외처리를 안해주면 결국 프로그램은 예외로인해 종료된다.
try with resource
파일연결객체의 사용후 연결종료는 매우 중요한, 꼭 해줘야할 행위인걸 알겠는데 너무 귀찮다….
저런 연결객체 선언, 인스턴스화, finally 종료코드를 모두 다 써주려면 족히 6~7줄은 필요하다.
하지만 try의 소괄호를 사용하면 간결하게 해결 가능하다.
try(FileReader fr = new FileReader(fileName);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);)
//try블럭전에 소괄호에 사용할 객체들을 선언하자, finally에서 삭제하지 않아도 자동으로 소멸된다.
{
int lineNumber = 1;
//BufferedReader생성자에서 Reader클래스를 요구한다. Reader의 자식인 FileReader를 넘겨주자.
String line = "";
line = br.readLine(); //파일의 끝을 만나면 null을 돌린다.
System.out.println(lineNumber++ + ": " + line);
while((line = br.readLine()) != null)
{
System.out.println(lineNumber++ + ": " + line);
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{ }
...
객체 선언과 생성도 try안에서! 연결해재를 위한 finally도 필요없다!
맨날 생성했으면 close하라고 경고문 띄우는 Scanner 객체에도 이 방법을 쓰면 더이상 경고하지 않는다.
try(Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);) {
...
}
catch(NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
일부러 발생시키는 예외
이번엔 일부러 예외를 발생시키는 코드를 알아보자
try {
System.out.println("1");
throw new NullPointerException("일부러 예외발생");
//개발자가 강제로 예외객체 생성후 발생시키는 구문
}
catch(NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("2"); // 2
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 일부러 예외발생
}
처리하지 않으면 프로그램이 종료되는 예외도 있지만 개발자가 직접 예외를 설정할 떄도 있다.
예를들어 시험점수 입력 프로그램을 만들때 시험점수가 100점보다 크면 이상하지 않은가
이럴경우 자신이 만든 예외클래스로 예외를 발생시킨다.
class ScoreOutOfBoundException extends Exception //점수를 넘어갈때 발생할 예외의 클래스선언!
{
private final int ERR_CODE;
public int getERR_CODE() {
return ERR_CODE;
}
public ScoreOutOfBoundException() {
this.ERR_CODE = 1001;
}
public ScoreOutOfBoundException(String message) {
this(message, 1001);
}
public ScoreOutOfBoundException(String message, int errCode) {
super(message);
this.ERR_CODE = errCode;
}
}
예외클래스는 Exception클래스를 상속해야 한다. Exception으로부터 message라는 멤버변수를 상속받는다.
errCode를 따로 주지 않는 이상 ERR_CODE를 모두 1001로 초기화하도록 생성자를 정의!
개발자가 발생할 예외를 ERR_CODE에 정수로 표현할 수 있다.
message를 받으면 Exception의 생성자에 message를 넘기면서 message값 초기화!
그리고 예외처리가 되는 점수입력용 클래스를 하나 만들자
class Score {
private int kor;
public int getKor() {
return kor;
}
public void setKor(int kor) throws ScoreOutOfBoundException {
if(kor >=0 && kor <=100) this.kor = kor;
else throw new ScoreOutOfBoundException("국어점수 벗어남");
}
}
setKor(int kor)메서드를 보면 new 예외클래스(message) 로 예외객체를 생성해서 throw한다.
좋은 클래스를 선언하려면 항상 멤버변수에 예상치 못한 값이 들어오면 예외처리를 해줘야한다.
왜 안에서 try catch로 예외를 잡지 않고 밖으로 throw하냐면 이상한 값을 넣은 밖의 코드가 잘못이기때문….
오류 발생원인을 제공한 코드가 예외를 잡는것이 일반적이다.
Score score = new Score();
try {
score.setKor(101);
} catch (ScoreOutOfBoundException e) {
System.out.println(e.getERR_CODE()); // 1001
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 국어점수 벗어남
System.out.println(e.toString()); // days19.ScoreOutOfBoundException: 국어점수 벗어남
}
다양한 방법으로 예외객체의 message를 출력할 수 있다.